I had a discussion recently with a leading game studio about fraud. We see an alarming trend has emerged: the gaming industry has become a prime target for fraudsters, as in every community, online or offline, there is fraud.
In the vast landscape of the gaming industry, the numbers speak volumes: there are more players, game titles, and competitions than ever before. A new era has dawned, where gamers come from diverse backgrounds, encompassing all genders.
Particularly during times of social isolation, gaming has thrived, giving players the opportunity to have community-oriented experiences. Because of this, the gaming industry is now stronger than it has ever been.
The financial statistics clearly show this. Presently, the video game market is valued at a staggering US$365 billion, exhibiting an impressive annual growth rate of over 7%. Looking ahead, experts project the market volume to reach US$482 billion by 2027, as emerging technologies such as the Metaverse, GameFi, VR, and AR mature.
In this article, I want to share some insights from my work at 5CA and lectures at the University of Amsterdam about fraud. Fraud in this context is ‘intentional deception to secure unfair or unlawful gain, or to deprive a victim of a legal right’.
How does fraud work?
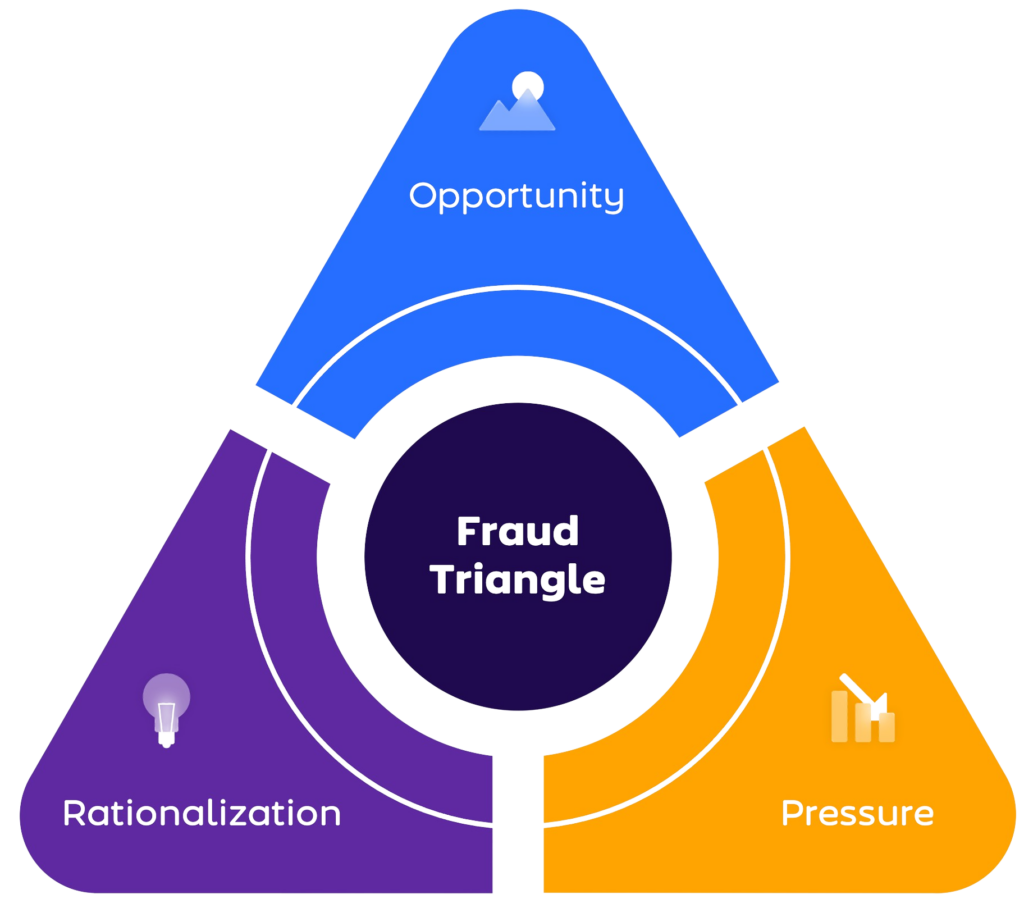
In our opinion, when fraud occurs, three elements come together in the so-called Fraud Triangle:
- The How: Opportunity. This refers to the circumstances that allow fraud to occur. Without it, fraud becomes impossible, so we focus (internal) controls on this part which is called prevention.
- The Why: Pressure. The usual financial need on the part of the fraud perpetrator is referred to as pressure, motive, or incentive. It is the reason why a person commits fraud. Screening of employees and looking for signs of misconduct can help identify this element.
- Rationalization. The most difficult part to observe is rationalization of committing fraud and involves fabricating a moral excuse to justify the fraud. We believe nurturing the right culture and ethical values reduces the rationalization of undertaking fraudulent actions.
Breaking the Fraud Triangle is the key to fraud deterrence. Breaking the Fraud Triangle implies that an organization must remove one of the elements in the fraud triangle to reduce the likelihood of fraudulent activities.
What types of fraud are there?
Looking at specific types of fraud, we can define use-cases to prevent and detect them sooner. In the gaming industry, we identify the following specific types of fraudulent behavior.
In-Game Fraud
- Hacking and Cheating: Individuals employ hacking techniques and cheat codes to gain unfair advantages in online multiplayer games. This undermines fair competition and spoils the gaming experience for honest players.
- Account Theft: Cybercriminals target gamers by stealing their account information, compromising their virtual assets, and even selling or trading them on the black market.
- Charge backs and Returns: incidents whereby customer support agents have a great understanding of the chargebacks/returns process which they are then able to maliciously abuse to process their own fraudulent transactions.
- Multi Accounting fraud: a single person creates two or more fake user-accounts with player profiles to compete against themselves, for example in online tournaments, thereby controlling the entire game and creating manipulative attack methods.
Virtual Currency and Item Scams
- Phishing: Fraudsters create deceptive websites or send phishing emails claiming to offer free virtual currency, rare items, or cheats. Unsuspecting players fall into their traps, providing sensitive information that leads to account theft or financial losses.
- Fake Online Marketplaces: Fraudulent platforms promising discounted or exclusive in-game items entice players into making purchases. However, these items either never materialize or are inferior counterfeits, leaving players cheated and frustrated.
- Boosting levels and battle pass ranks can impact a developer’s financials as well as make an unfair landscape for the player base.
Loot Boxes and Gambling
- Predatory Monetization: Some game developers implement loot boxes or similar mechanics, which are akin to gambling, without providing clear odds or transparency. This practice targets vulnerable players, potentially leading to addictive behaviors and financial losses.
- Skin Betting: Skin betting, where players use virtual item skins as currency in online gambling, blurs the line between gaming and gambling, often targeting minors and causing regulatory concerns.
Third-Party Marketplaces
- Unauthorized Reselling: Unauthorized third-party websites allow players to buy and sell in-game items, currencies, or accounts. However, these platforms lack regulation, making players susceptible to scams, fraud, and unfair transactions.
- Real-World Trading: Some players engage in real-world trading by selling virtual items for real money. This practice not only violates the terms of service of most games but also exposes players to fraud risks.
Fraud deterrence: how to effectively combat fraud
As with all risks, we must realize that we can never 100% prevent fraudulent behavior. But we can do a lot to prevent and minimalize the risk and, when fraud does occur, detect it in an early stage so we can respond accordingly.
- Enhanced Security Measures. We advise implementing a so-called Zero-Trust environment with multi-factor authentication, improved encryption, and security monitoring systems to protect player accounts from unauthorized access and hacking attempts.
- Reporting and Moderation Systems. Robust and near real-time data driven reporting and moderation teams help detect and identify fraud and enables players to report fraudulent suspicious activities, ensuring quick action against offenders.
- Education and Awareness. Gaming and BPO companies, communities, and influencers are raising awareness about fraud risks, teaching agents and players about safe practices, and advising them on how to identify and report fraudulent activities.
- Employee screening. Screening employees, in our case customer support agents and staff, on hiring and periodically can help identify possible risks, as mentioned above in the ‘why’ part of fraud.
- Nurture a ‘just culture’. This is a culture that asks the questions of what went wrong more than who went wrong. This helps people feel humanized and part of the team rather than the reason of a fault. A just culture helps create an environment where individuals feel free to report errors and help the organization to learn from mistakes. This contrasts with a “blame culture” which prevents learning from mistakes.
Conclusion
Fraud is a significant challenge within the gaming industry, threatening the integrity of player experiences. From hacking and cheating to virtual scams and predatory practices, fraud takes various forms and impacts players on multiple levels.
Collaboration between BPO companies, game developers, agents, players, and regulatory bodies is key to ensure a safer and more transparent gaming environment.
By taking the measures as described above, we can already reduce the risk significantly and keep improving the safe and secure environment needed.
At 5CA we have a unified Microsoft Platform Foundation, based on Zero-Trust Architecture, providing a compliant environment with security and privacy by design. This enables us with the right combination of security measures and controls, data driven reporting and monitoring allowing us to prevent, detect and respond in the best way possible. In our opinion, this leads to the best synergy between our great people, the best tools and actionable insights.
About the author
David Bos, an avid gamer and Star Wars enthusiast with over 23 years’ experience in serving global customers. Currently CTO at 5CA, former Deloitte CTO and technology leader. Part-time Lecturer Amsterdam University on Data & AI and Cyber Security.
Specialized in Technology, Innovation, Data & AI, Automations and Cyber Security.